Historical Human Migration
From Ancient Movements to Modern Immigration
Historical Human Migration
Learn phrasal verbs naturally while exploring the fascinating story of human migration across history
Historical Journey
Ancient Migrations to Modern Immigration
You are hereCurrent Patterns
21st Century Migration & Global Challenges
Start LearningCultural Perspectives
Diverse Views on Human Movement
Start Learning🎯 Your Learning Progress
0%A Historical Approach to Human Migration
🎧 Listen, watch and practice with real-time shadowing
🎭 Practice Shadowing
Shadowing is a language learning technique where you listen to native speakers and repeat simultaneously, mimicking their pronunciation, rhythm, and intonation. This method improves speaking fluency and natural accent.
Complete Hub • Exercises • Shadowing
🎙️ Video Podcast
🎧 Audio Version
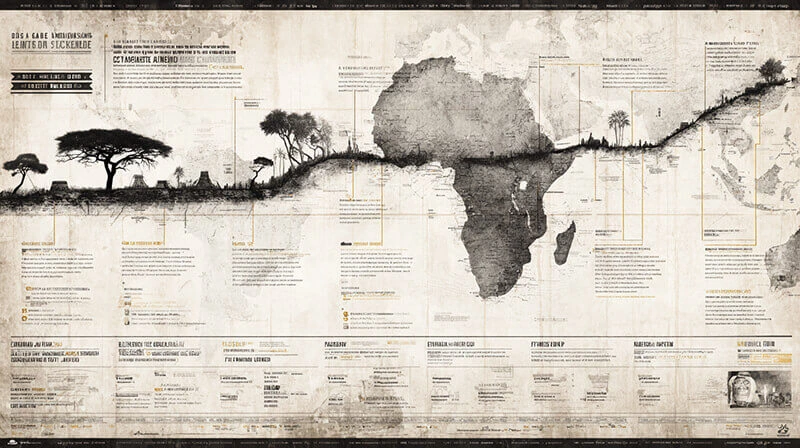
🌍 Timeline: From Ancient Movements to Modern Immigration
Key Periods in Human Migration History
🚶 The Dawn of Human Movement

Since the beginning of time, humans have been setting out from their original territories to explore new lands. Our ancestors set off on journeys that would bring about the colonization of entire continents. Archaeological evidence shows that early humans moved away from Africa around 70,000 years ago, taking on the challenge of adapting to completely different environments.
These early migrations came about due to various factors: climate changes brought on food shortages, population growth led to resource competition, and natural curiosity drove people to look for better opportunities. As groups spread out across the globe, they ran into other communities, sometimes getting along peacefully, other times fighting off territorial disputes.
The process of human expansion carried on for thousands of years. Each generation passed down knowledge about migration routes and survival techniques. Communities would break up when resources became scarce, with some members moving on to establish new settlements while others stayed behind to maintain ancestral lands.
🏛️ Early Civilizations and Population Exchanges
As civilizations built up along rivers and fertile lands, migration patterns took on new characteristics. The development of agriculture brought about permanent settlements, but this didn't put an end to human mobility. Instead, it gave rise to different types of movement: seasonal migrations, trade expeditions, and territorial conquests.
Ancient civilizations set up complex networks that linked up distant regions. Merchants set out on long journeys, carrying out trade that brought together diverse cultures. The Silk Road came into being as various routes joined up to connect East and West, allowing ideas and populations to mix together.
When conflicts broke out, entire populations were forced to move away from their homelands. Winners would drive out the defeated, forcing them to start over in unfamiliar territories. These early patterns of forced migration laid the groundwork for more systematic forms of population displacement that would show up in later historical periods.
🌍 Exercise: Human Migration and Movement
Click on the blank spaces to choose the correct answer
Take a break from history
Explore more learning resources while the medieval knowledge settles in
Halfway through! 🎉
You're doing great! Ready to explore more amazing content?
⚔️ The Roman Empire and Systematic Population Displacement
The Roman Empire brought about the first large-scale systematic displacement of populations. As Roman legions moved in to conquer new territories, they didn't just take over lands – they carried out deliberate policies to break down existing social structures and mix up populations.
Romans set up colonies throughout their empire, bringing in settlers from other regions to fill up newly conquered areas. They would move out local leaders and put in Roman administrators. This strategy worked out well for maintaining control, as it cut down on local resistance and built up loyalty to Rome.
The empire also took on massive infrastructure projects that brought together workers from across the Mediterranean. Roads and aqueducts linked up distant provinces, making it easier for people to get around and settle down in new areas. When the empire eventually fell apart, these established migration routes carried on being used by subsequent civilizations.
Slavery made up a significant portion of Roman population movements. Conquered peoples were rounded up and shipped off to work in different parts of the empire. This system brought on the forced migration of millions, setting up patterns that would unfortunately carry over into later historical periods.
🏰 Medieval Movements and Religious Migrations
During the medieval period, migration took on religious and cultural dimensions. The spread of Christianity and Islam brought about massive population movements as people set out to spread their faith or escape religious persecution. Pilgrimage routes opened up new pathways for cultural exchange.
The Crusades brought together armies from across Europe who set off for the Holy Land. These military expeditions stirred up centuries of conflict but also brought about increased contact between different civilizations. Trade routes that had dried up after Rome's fall began to pick up again.
Mongol invasions brought on some of the largest forced migrations in history. Entire populations moved away from advancing armies, starting over in distant lands. However, the Mongol Empire also set up the largest continuous land empire in history, linking up East and West in unprecedented ways.
Viking expeditions opened up new migration routes to the north. These seafaring peoples set out from Scandinavia and spread out across Europe, setting up settlements from Iceland to Russia. Their movements brought about the colonization of previously uninhabited lands and mixed together Nordic culture with local traditions.
⚓The Age of Exploration and Colonial Expansion
The 15th and 16th centuries brought about a new era of migration driven by European exploration and colonization. European powers set out to find new trade routes and ended up discovering entire continents. This period brought on unprecedented global population movements.
Portuguese and Spanish explorers opened up sea routes to the Americas, Asia, and Africa. These expeditions set off a wave of colonial expansion that would bring together peoples from different continents for the first time. European settlers moved in to establish colonies, often driving out indigenous populations or forcing them to give up their traditional lands.
The colonial period set up plantation economies that brought about the demand for massive amounts of labor. This economic system led to one of the darkest chapters in human migration history: the Atlantic slave trade. European colonizers turned to Africa to fill up their labor needs, setting in motion a forced migration that would go on for over three centuries.
Colonial powers worked out complex systems to bring over settlers, indentured servants, and enslaved peoples. These migrations brought together African, European, and indigenous American populations, giving rise to new mixed cultures and societies that made up the foundation of modern American nations.

🌍 Phrasal Verbs das Migrações Humanas (18 verbos)
⛓️ The Atlantic Slave Trade and Forced African Migration
European slave ships set out from ports along the African coast, loaded up with human cargo. The Middle Passage brought on unimaginable suffering as enslaved Africans were packed in under inhumane conditions. Many didn't make it through the journey, while survivors ended up on plantations throughout the Americas.
The slave trade set up a triangular system that linked up Europe, Africa, and the Americas. Ships would set off from Europe loaded up with manufactured goods, trade them for enslaved people in Africa, then carry them to the Americas where they were sold off for raw materials that were shipped back to Europe.
Despite the brutal conditions, enslaved Africans held onto their cultural traditions and worked out ways to pass them down to future generations. They came up with new forms of music, religion, and social organization that brought together African traditions with American influences. These cultural innovations would later spread out and influence global culture in profound ways.
Take a break from history
Explore more learning resources while the medieval knowledge settles in
🏭 Industrial Revolution and Modern Immigration Patterns
The Industrial Revolution brought about dramatic changes in migration patterns. As factories sprang up in cities, they drew in workers from rural areas. This period set off the first major rural-to-urban migrations in history, as people moved away from agricultural work to take on industrial jobs.
Economic opportunities in industrializing countries brought in millions of immigrants. The United States opened up its borders to European immigrants who were looking for better lives. Ellis Island processed over 12 million immigrants who had set out from Europe hoping to start over in America.
Railroad construction opened up vast territories and brought about new settlement patterns. The transcontinental railroad linked up the American coasts and brought in workers from China and other countries. These projects mixed together diverse populations and set up multicultural communities.
Labor shortages brought on by industrial expansion led to recruitment of workers from distant countries. Companies would send out agents to sign up immigrants, often making up promises about working conditions. This period saw the rise of organized immigration that brought together people from all corners of the globe.

💼 Contemporary Immigration: Globalization and Modern Displacement
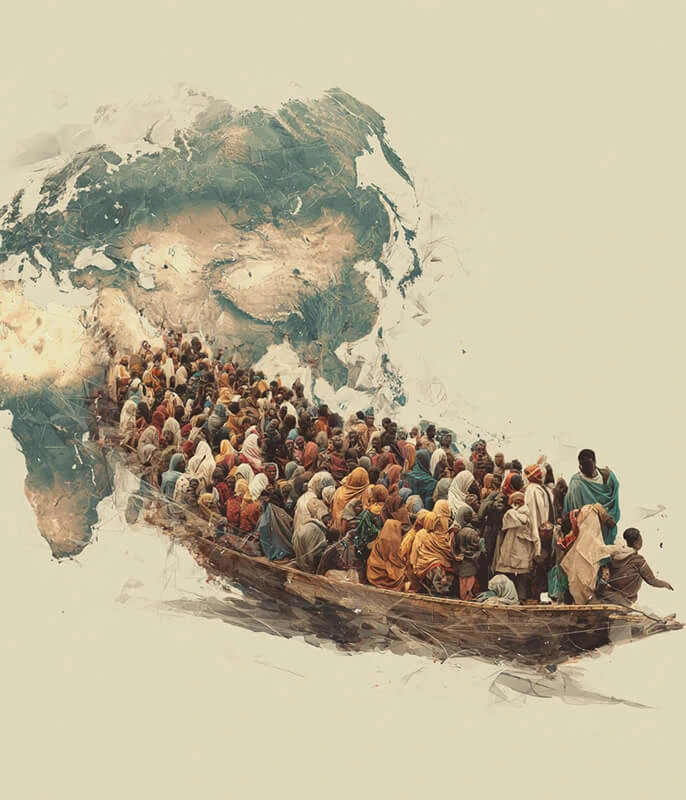

Modern immigration patterns have taken on new characteristics in our globalized world. Economic opportunities draw in skilled workers who can move around more easily than ever before. Technology has opened up new possibilities for people to stay connected with their home countries while setting up new lives elsewhere.
Political conflicts continue to bring about forced migrations. Wars drive out millions of people who must flee from violence and seek out safety in other countries. Climate change is bringing on new forms of displacement as rising sea levels and extreme weather force people to move away from their traditional homes.
Globalization has brought together labor markets worldwide. Multinational companies set up operations across borders and bring over workers with specialized skills. This has given rise to a new class of global migrants who move around frequently for career opportunities.
However, modern immigration has also brought on new challenges. Many countries have tightened up their border controls and put in place stricter immigration policies. This has led to dangerous migration routes where people risk their lives to get across borders. The situation has brought about humanitarian crises that require international cooperation to sort out.

🎯 Conclusion: The Continuing Story of Human Movement
Throughout history, human migration has been a constant force that has shaped our world. From the earliest humans who set out from Africa to modern immigrants who move around in our globalized economy, the story of migration shows how movement and cultural exchange bring about progress and innovation.
The patterns we've looked at demonstrate that migration comes about due to various factors: economic opportunities draw people in, conflicts drive them out, and human curiosity leads them to explore new possibilities. Each wave of migration has brought together different cultures and given rise to new forms of art, technology, and social organization.
Understanding this historical perspective helps us work out better policies for contemporary immigration challenges. As we move forward into the future, we need to take into account the lessons history has taught us about the benefits and challenges that come with human movement. The story of migration goes on, and how we deal with it will determine the kind of world we pass on to future generations.
Migration has always been part of the human experience. As we face new challenges like climate change and global inequality, we need to come up with innovative solutions that take advantage of the positive aspects of migration while addressing its challenges. The movement of people brings about the exchange of ideas, skills, and cultures that make up the rich tapestry of human civilization.
Congratulations! 🌟
You've completed this journey! Where would you like to explore next?
